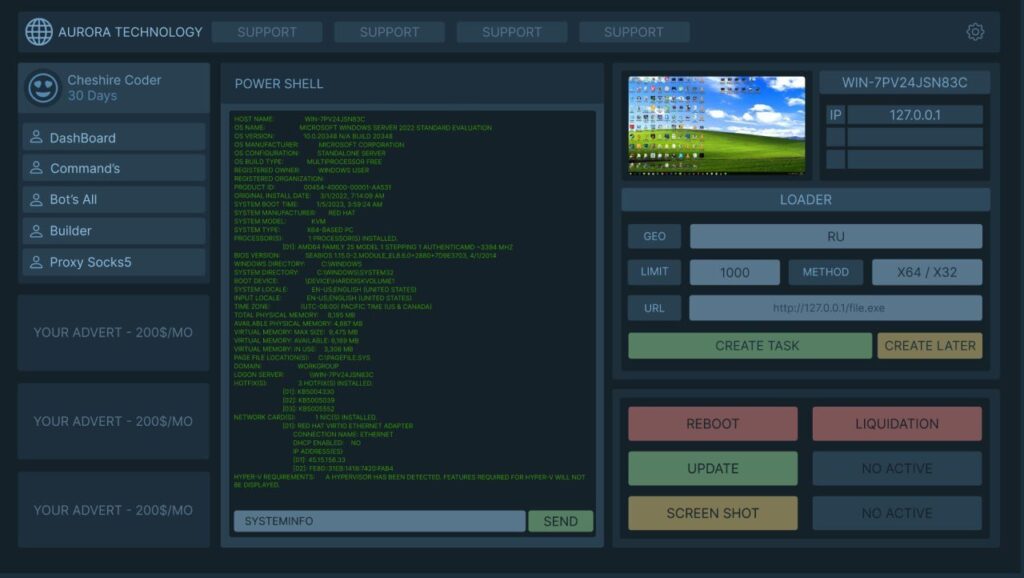
Aurora Stealer Background
Aurora Stealer a non-friendly program in your neighborhood is developed in Go-lang. The malware was developed for threat actors to steal victims’ sensitive data. Since its initial release, there have been many adaptations to the malware. It started as a botnet having info-stealer capabilities but currently it is a full-time info-stealer which is being sold by the threat actor labelled Cheshire on Russian speaking dark-net forums mentioned by cybersecurity firm Sekoia.
The malware has a knack for stealing the victim’s browser data including cookies, passwords, login data and many more. It has the horizon to steal data from most browsers. The stealer also targets crypto wallets to pilfer victim’s data. The malware does not stop here, it can exfiltrate files and data stored in different software from the victim’s machine. Once all the super-sensitive data is possessed by the stealer it delivers the data to the attacker.
Operating Model
The malware is being spread among victims in the hospitality industry through phishing emails as seen by Trendmirco. Besides phishing campaigns, the threat actors also have utilized SEO poisoning technique to deliver the malware via malicious ads of notepad++ according to SANS finding.
Upon the detonation of the malware, our observations revealed the implementation of multiple sophisticated techniques by the malware to evade detection by antivirus software. One such technique involved the incorporation of binary padding, resulting in an increase in the file size allowing the malware to circumvent the antivirus software and evade detection.
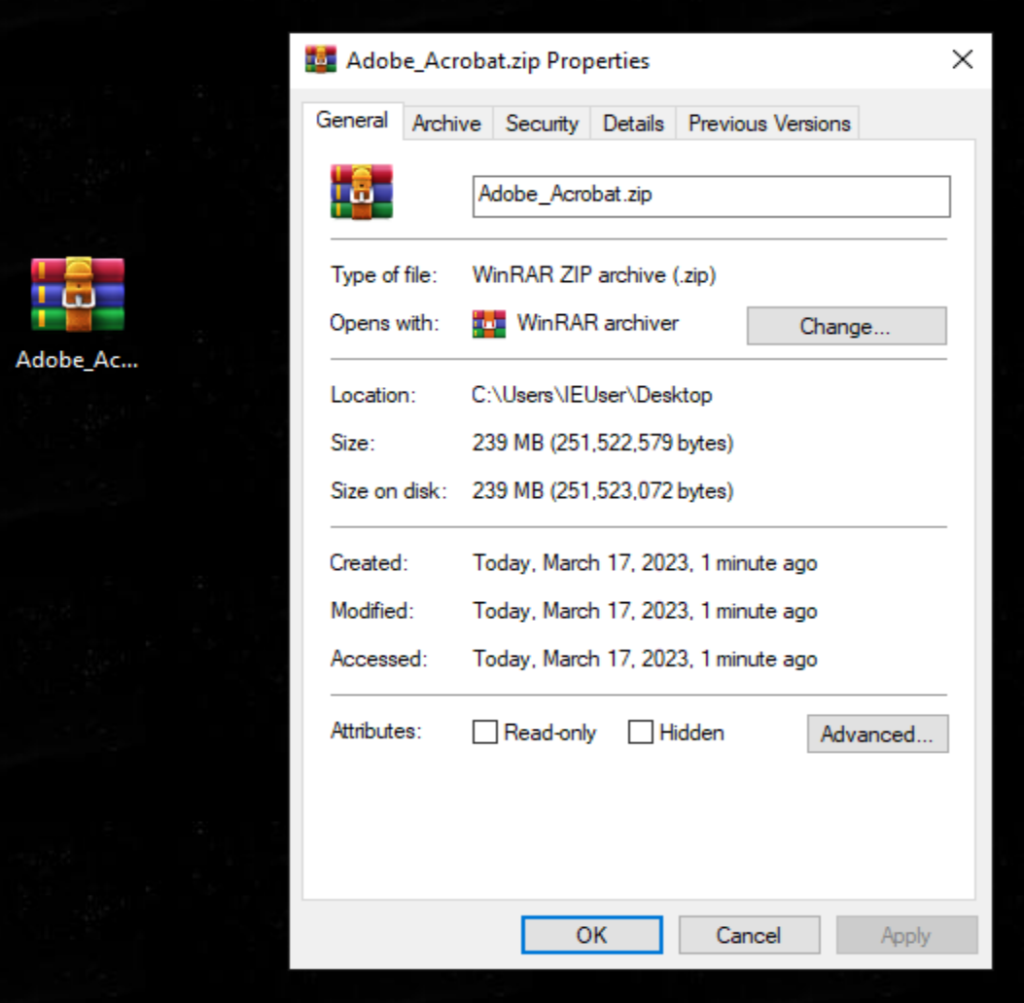
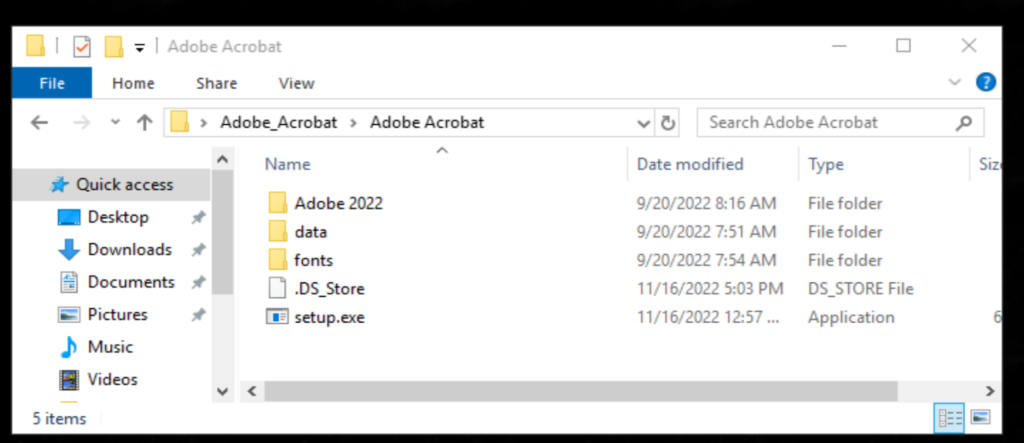
Figure2: Fake Adobe Acrobat Installer Downloaded from SEO Poisoning Campaign
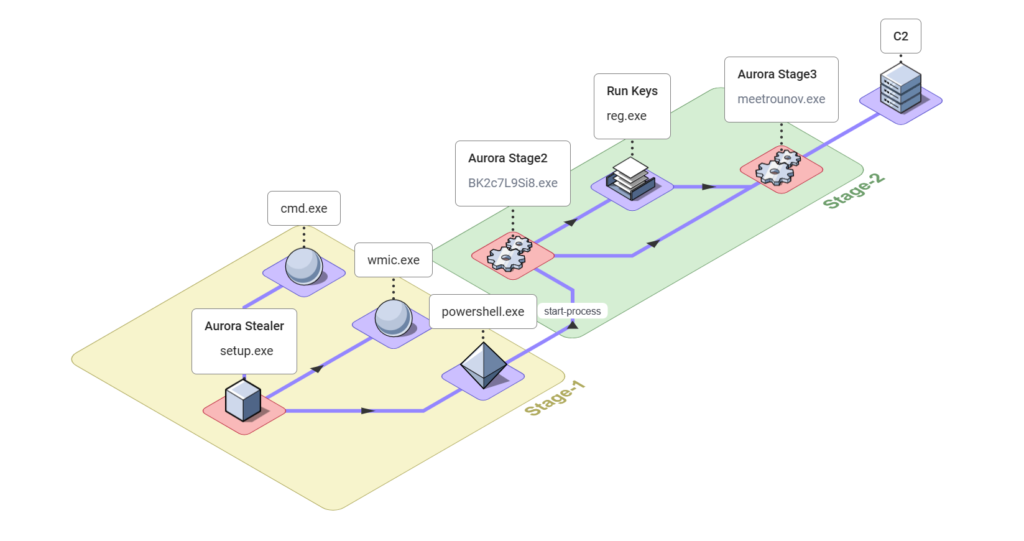
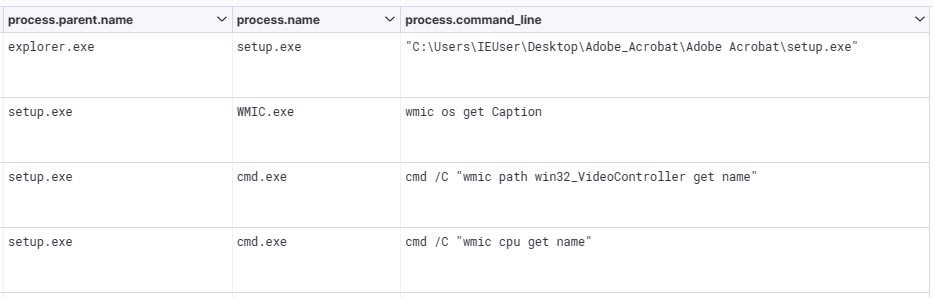
After successful infiltration, the malware utilizes Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) commands to gather pertinent system information. This behavior was consistently observed in all samples of Aurora stealer that we analyzed. Additionally, independent research conducted by Cyble and other industry experts has reported this observation.
We also captured Aurora stealer’s actions that were aimed at extracting sensitive information from files and folders located in various browsers, cryptocurrency wallets, and drives, as illustrated below.
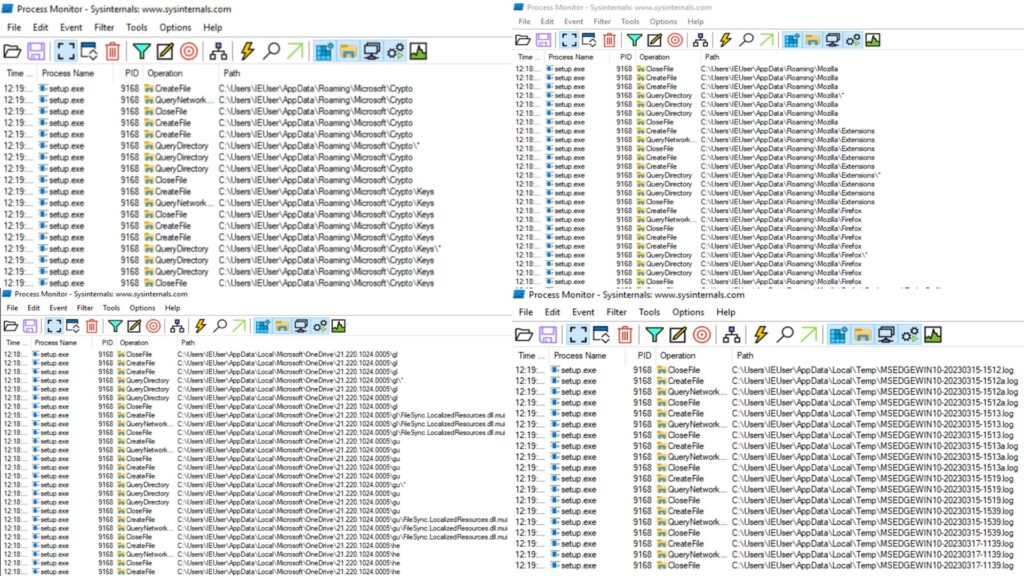
Aurora leverages PowerShell to facilitate the execution of its second stage, employing the following command:
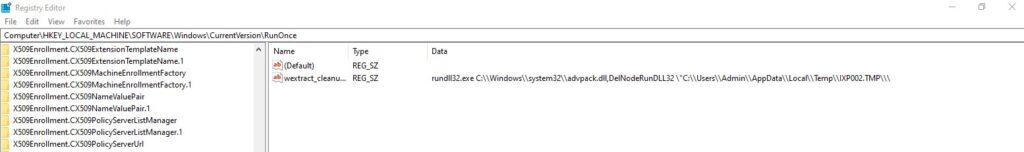
powershell "" "start-process C:\Users\Admin\AppData\Local\Temp\BK2c7L9Si8.exe" During the second stage of Aurora, an entry to the “run keys” in the registry was observed, enabling the malware to automatically execute its third stage DLL via RUNDLL32.exe at each user login.
The third stage of the malware executes an encoded PowerShell command allowing it to delay execution for certain duration using the following command before it exfiltrates the data to the attacker.
C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe" -enc UwB0AGEAcgB0AC0AUwBsAGUAZQBwACAALQBTAGUAYwBvAG4AZABzACAAMwA0AA==Once all the data and information are collected, the malware employs advanced encoding techniques to conceal the information and prepare it for shipment to the attacker over the C2 channel. The attacker can retrieve the encoded data and use it for nefarious purposes, such as identity theft or financial fraud.
Detection
The infernal behavior of this malware can be detected using SIGMA rules.
To begin with, we attribute different WMI commands getting executed in sequence to detect Aurora Stealer malware.
logsource:
category: process_creation
product: windows
detection:
selection:
Image|endswith: '\wmic.exe'
CommandLine|contains:
- 'wmic os get Caption'
- 'wmic path win32_VideoController get name'
- 'wmic cpu get name'
condition: selection
One detection would be to capture changes in ‘run key’ registry which execute DLL using RUNDLL32.exe
logsource:
product: windows
category: registry_set
detection:
selection:
EventType: SetValue
TargetObject|contains: '\REGISTRY\MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\RunOnce'
Details|re: .*rundll32.exe.C:\\\\Windows\\\\system32\\\\advpack.dll,DelNodeRunDLL32 \\"C:\\\\Users\\\\.*\\AppData\\\\Local\\\\Temp\\\\IXP[0-9]{1,3}.TMP.*
condition: selection
Based on the general behavior followed by Aurora and different malwares, we have developed several detection methods. We also observed changes in the configuration of Windows Defender, where the path ‘C:\Program Data’ is excluded.
logsource:
product: windows
category: registry_set
detection:
selection:
EventType: SetValue
TargetObject|contains: '\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Exclusions'
Details: 'C:\Program Data\'
condition: selection
Another detection would be by tracing event id `5007`, which can be activated by enabling Windows Defender operation logs. This particular event is triggered whenever there is a modification made to the configuration of Microsoft Defender Antivirus.
logsource:
product: windows
service: windefend
detection:
selection:
EventID: 5007
NewValue|contains: 'C:\Program Data\'
condition: selection
Additionally, one clever way to detect this malware is to monitor the execution of obfuscated PowerShell commands.
The same campaign can be detected using OSQUERY rules. Below are some rules that will help you keep your organization safe.
query_wmic:
SELECT name,
pid,
cmdline,
path,
parent
FROM processes
WHERE LOWER(name) = 'wmic.exe'
AND
(
cmdline LIKE '%OS Get Caption%'
OR cmdline LIKE '%path win32_VideoController get name%'
OR cmdline LIKE '%cpu get name%'
);
query_regsitry:
SELECT key,
path,
name,
type,
data
FROM registry
WHERE path LIKE 'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\\Software\\Microsoft\\Windows\\CurrentVersion\\RunOnce\\%'
AND data LIKE '%rundll32.exe C:\\Windows\\system32\\advpack.dll,DelNodeRunDLL32 "C:\\Users\\%\\AppData\\Local\\Temp\\IXP%.TMP\\%';
query_exclusion:
SELECT key,
path,
name,
type,
data
FROM registry
WHERE path LIKE 'HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Exclusions\Paths\%'
AND
(
data LIKE '%c:\programdata%'
OR data LIKE '%\appdata\roaming\microsoft\windows\start menu\programs\startup%' For more threat analytics reach us here.
The above rules have been vindicated by simulating Aurora stealer in a sandbox environment.
MITRE ATT&CK Techniques
| Tactic | Technique ID | Technique Name |
| Execution | T1204 T1059.001 T1059.003 T1047 | User Execution Command and Scripting Interpreter: PowerShell Command and Scripting Interpreter: Windows Command Shell Windows Management Instrumentation |
| Persistence | T1547.001 | Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder |
| Defense Evasion | T1562.001 T1027 T1218.011 T1497 | Impair Defenses Obfuscated Files or Information System Binary Proxy Execution: Rundll32 Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion |
| Credential Access | T1555.003 T1056 T1003 T1528 T1539 T1552.002 | Credentials from Password Stores: Credentials from Web Browsers Input Capture OS Credential Dumping Steal Application Access Token Steal Web Session Cookie Credentials in Registry |
| Discovery | T1087 T1083 T1012 T1082 T1518.001 T1614 T1497 | Account Discovery File and Directory Discovery Query Registry System Information Discovery Software Discovery: Security Software Discovery System Location Discovery Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion |
| Collection | T1119 T1005 T1056 T1113 | Automated Collection Data from Local System Input Capture Screen Capture |
| Command and Control | T1071.001 T1105 T1095 T1571 | Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols Ingress Tool Transfer Non-Application Layer Protocol Non-Standard Port |
Threat Bites
Threat Actor
Targeted Country
Targeted Industry
First Seen
Last Seen
LOLBAS
Telemetry
Samples
:
:
:
:
:
:
:
:
Unknown
Worldwide
Hotels
April 2022
March 2023
Wmic, Reg, Rundll32
Sysmon, Security, Windefend, PowerShell
References
- https://blog.sekoia.io/aurora-a-rising-stealer-flying-under-the-radar/
- https://blog.cyble.com/2023/01/18/aurora-a-stealer-using-shapeshifting-tactics/
- https://www.trendmicro.com/vinfo/us/threat-encyclopedia/spam/3721/fake-roadway-map-leads-to-aurora-stealer
- https://isc.sans.edu/diary/rss/29448
- https://cyware.com/news/botnet-turned-infostealer-aurora-gaining-traction-among-threat-actors-2db2171d
Author: Saharsh Agrawal
Security Researcher, Loginsoft